StandardReal Estate Commission Calculator (Spilt or Flat Fee)
Step 1
Enter your commission details:
Step 2
Enter your agent commission plan:
Waiting for data entry...
Here are your final net payables:
Enter your commission details:
Enter your agent commission plan:
Here are your final net payables:
Enter your commission details:
Enter your agent commission plan:
Here are the details of the commission tier amounts:
Here are your final net payables:
Real estate commissions can be tough to calculate. Complex structures, agent fees, and varying rates make figuring them out a time-consuming process. It’s easy to put these calculations on the back burner and focus on other parts of running your brokerage.
But it’s essential to keep on top of how much you owe. Knowing the amount you need to pay agents well in advance helps you make better financial projections, ensuring payday has no surprises.
You could calculate commission manually. But if you want an easy-to-use shortcut, try our free real estate commission calculators. They will tell you exactly how much to pay your agents for each sale they get over the line.
We have created two real estate agent commission calculators. They help with both split and tiered commission structures—these are the payment plans used by the majority of real estate brokerages and agents.
💰 Real Estate Commissions Explained — Everything you need to know about real estate commissions.
🧾 How to Calculate Commission in 4 Easy Steps — Simple commission plan? Follow these steps to learn how to calculate commissions quickly.
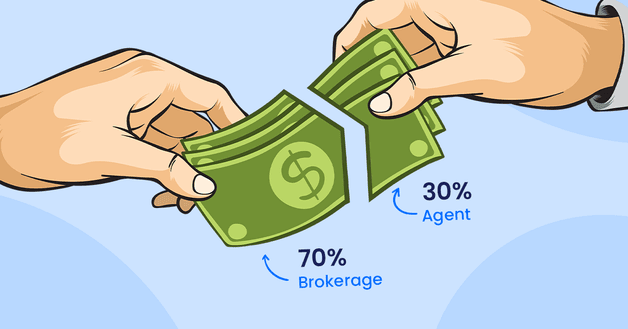
A common agent/broker commission split is 70/30. In this case, 70% of the commission on a sale goes to the brokerage and 30% to the agent.
Imagine an agent makes a sale worth $420,000. Of this selling price, 3% (or $12,600) goes to the selling side.
In a 70/30 split, the agent would receive $3,780 and the brokerage would get $8,820.
Then the agent’s fees would come off their commission. Let’s say they are $300. The agent’s final commission is now $3,480, while the brokerage gets $9,120.
There are four main figures you must know when calculating a standard split commission.
These are:
Once you know all the above figures, you can calculate how much you need to pay the real estate agent for each sale.
Tiered commission structures are when the agent receives a different percentage of the total commission depending on how much they earn in a specific period.
This type of structure incentivizes real estate agents to make more sales by giving them a larger piece of the pie when they do so.
But they are more complicated than split commission structures. This is because the amount of commission the brokerage pays the agent changes once the agent hits a predefined threshold.
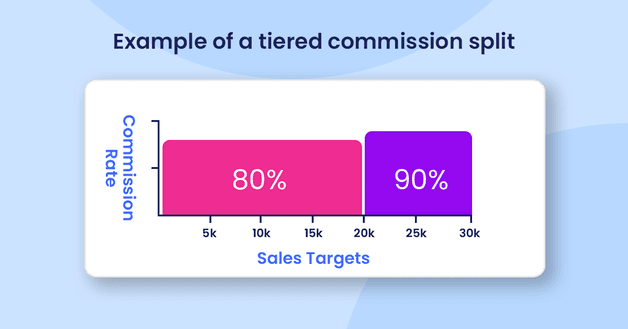
The agent and the brokerage could have a deal whereby the agent earns 80% of the total commission for the first $20,000 in commission they earn in a quarter. They may then earn 90% of commission for anything above this in the same period.
Say the agent had a productive quarter and bought in real estate commissions worth $29,000. Their take-home amount would be $24,100. That works out at $16,000 (80% of $20,000) plus $8,100 (90% of $9,000).
It’s easy to see how this type of commission structure motivates real estate agents. If the agent was on a flat fee commission structure of 80%, they would only have earned $23,200. That’s almost $1,000 less for the same amount of work.
The biggest challenge in calculating tiered commission is when a property takes the agent over the edge into the next commission level.
In this situation, calculate how much of the commission qualifies for the pre-threshold rate, and how much qualifies for the post-threshold rate.
You’ll also need to consider the agreement you have with each agent, as this will often vary depending on their experience and needs.
Another complicating factor is that these calculations are typically only used a few times a year when agents hit their targets. This means brokerages may not have much experience calculating them.
As well as the metrics listed in the flat fee commission structure section of this article, you also need to know:
You can use transaction management software alongside the real estate commission calculator to track the number and value of sales each agent makes.
💸 How To Create a Real Estate Commission Disbursement Authorization (CDA) — Learn how you can create commission disbursement authorizations for each closing with little effort.
You may need to consider other fees paid to third parties when using the real estate commission calculator.
Here are some of these fees. We’ll also explain how to take them into account when using the commission calculator.
Brokerages may set up partnerships with other brokerages to refer clients in exchange for a percentage of the sales commission.
This will often happen when a seller moves to a new area and is looking to buy a home. If the selling brokerage doesn’t have a presence in that area’s real estate market, they can recommend one that does.
Brokerage referral fees are typically taken out before the commission is split between the brokerage and the agent. However, this will depend on the exact deal you have set up with the referring brokerage.
Here’s an Example
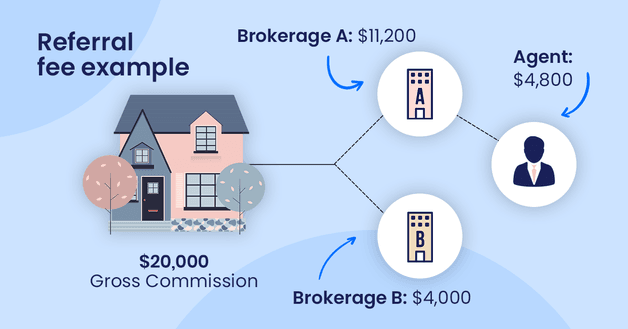
Brokerage A sold a property that was referred to them by brokerage B. The agreement stated that brokerage A has to give 20% of the total commissions to brokerage B.
As brokerage A received $20,000 in commission, it had to give $4,000 to brokerage B. The remaining $16,000 was split between the brokerage and the agent at the agreed-upon rate.
You can use the real estate commission calculator in this article to calculate how this remaining amount should be split.
Major brokerages often charge a “franchise fee” on sales made by franchise brokerages. Like referral fees, this is typically taken out before the commission is split between the broker and the agent.
Here’s an Example
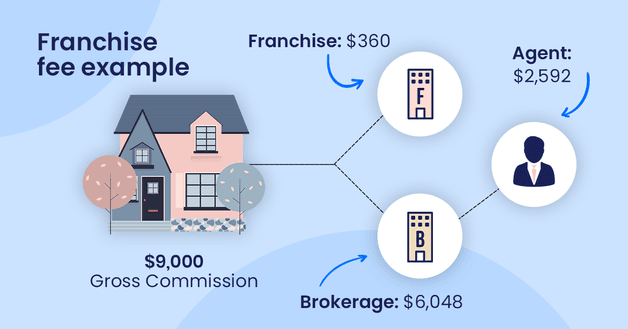
Brokerage A is a franchise of a major brand. It pays a fee of 4% of commission on every sale.
If the total commission earned from a sale was $9,000, $360 would go to the franchise. The remaining $8,640 would be split between the agent and brokerage as agreed.
Our real estate calculators are designed to work with split and tiered commission structures.
But these aren’t the only payment structures that brokerages use. Our tools can also help with commission structures like team splits and flat-fee models.
In a flat-fee model, real estate agents keep the entire commission. Instead of paying commission, they pay a flat monthly desk fee to the brokerage. This doesn’t change, whether they sell zero properties or ten.
This type of structure is beneficial for experienced real estate agents who don’t need much help generating leads or making sales. The lack of commission provides far more earning potential.
This structure can also benefit brokerages. They get a guaranteed and consistent income no matter how their agents perform. It may also attract more experienced agents.
Here’s how to calculate flat fee percentages using our commission calculator:
Following these steps will show you exactly how much you need to pay the agent. If the agent pays the desk fee in advance, you won’t need to make this calculation.
Brokerages that use a team split model share out the commission between everyone who works on the deal, not just the agent.
While this can see the agent take home considerably less per deal, the benefit is that the team can push more deals over the line. Many real estate agents make more money due to the higher volume of sales than they would if they worked independently.
Team splits add an extra layer of complication to the way real estate commissions are calculated. Typically the brokerage takes a cut first, and the rest is split between the agent and the team.
To use our tools to calculate a team split, we’d recommend that you use the standard split calculator to see how much the brokerage takes home and then manually calculate how the remaining income is split between the team.
👨💼👩💼 Sales Commission Structure: How Flat Fee, Splits and Thresholds Will Motivate Your Agents — Learn the common sales commission structures and how each one can affect agents’ motivation.
We use cookies to improve your experience, analyze website traffic, and provide personalized ads and content. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more in our cookie policy.